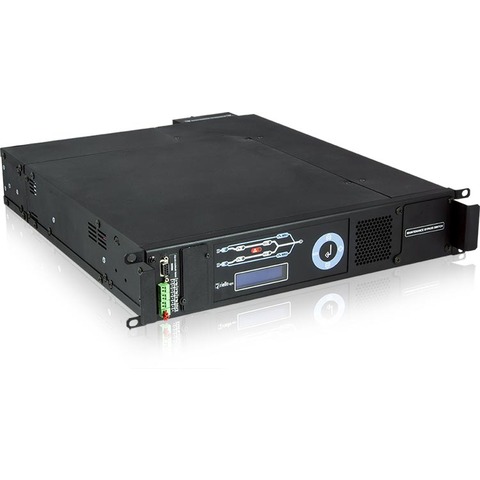
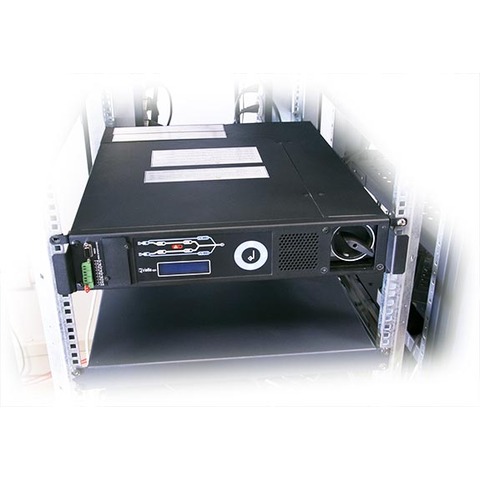
1-phase static transfer switch
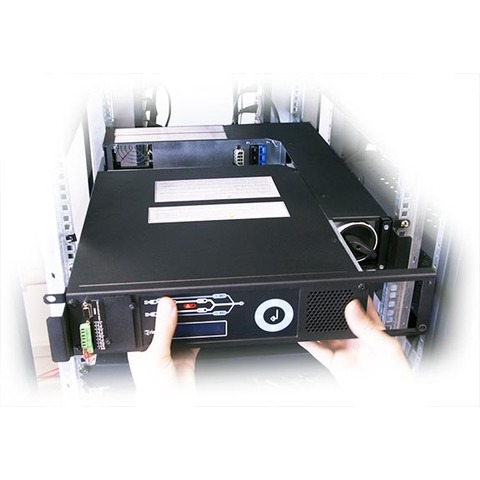
Master Switch Single-Phase is a transfer switch designed to protect loads with different power ratings. Choice of 3 sizes (32A, 63A, and 120A) and with a manual bypass to easily switch sources in the event of a fault.
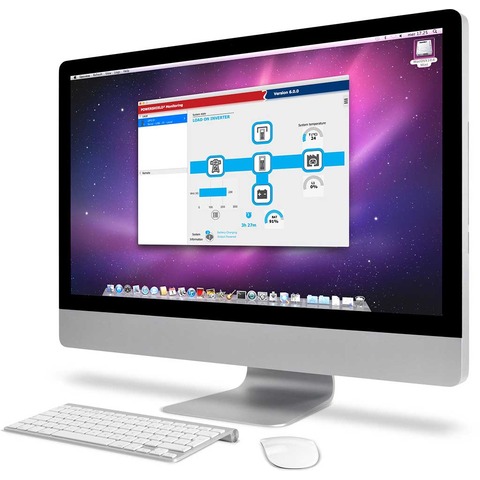
Complete Diagnostics
Features an LCD control panel with multi-functional keys. This enables you to monitor readings and switch operating statuses quickly and intuitively. Incorporates 3 dry contacts, RS232 port, and a communications slot to allow for further LAN connection.
Load Protection
Guaranteed switching time of less than a quarter of a cycle (< 4 msec for synchronised inputs; < 10 msec for non-synchronised). This is the case for both automatic and manually-triggered switches.